Tips and tricks, especially in the programming world, can be very useful.
Sometimes a little hack can be both time and life-saving.
A minor shortcut or add-on can sometimes prove to be a Godsend and can be a real productivity booster.
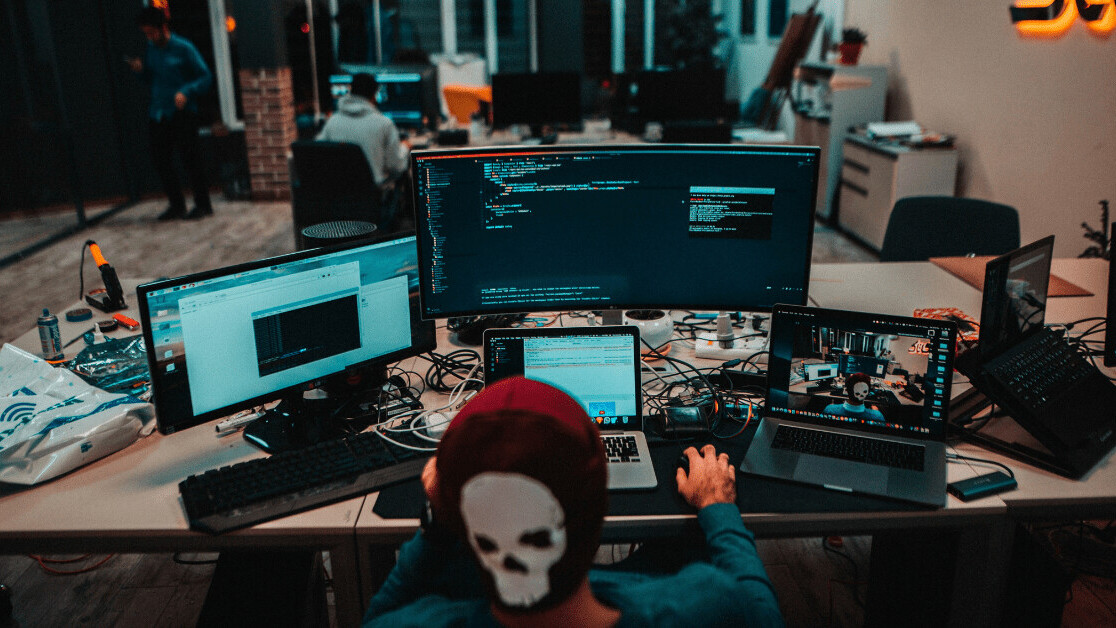

Its a simple and fast way to perform exploratory data analysis of a Pandas Dataframe.
The pandasdf.describe()anddf.info()functionsare normally used as a first step in the EDA process.
This single line of code is all you better display the data profiling report in a Jupyter notebook.
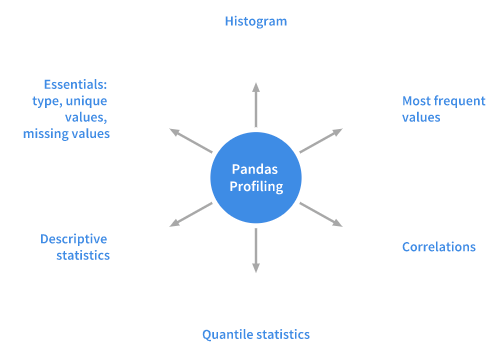
The report is pretty detailed including charts wherever necessary.
The report can also be exported into an interactive HTML file with the following code.
Refer to thisdocumentationfor more details and examples.

However, the visualizations rendered with this function arent interactive and that makes it less appealing.
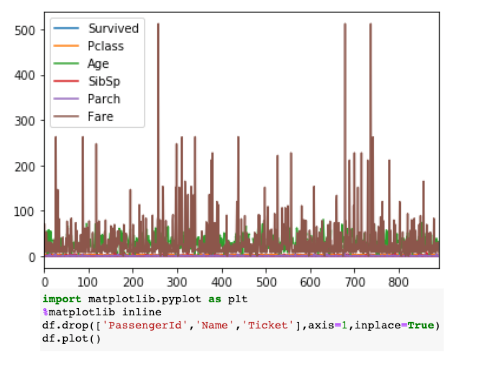
On the contrary, the ease to plot charts withpandas.DataFrame.plot()function also cannot be ruled out.
Well, you’ve got the option to actually do that with the help ofCufflinkslibrary.

Cufflinks library binds the power ofplotlywith the flexibility ofpandasfor easy plotting.
Lets now see how we can load the library and get it working in pandas.
Time to see the magic unfold with the Titanic dataset.

Click herefor more examples.
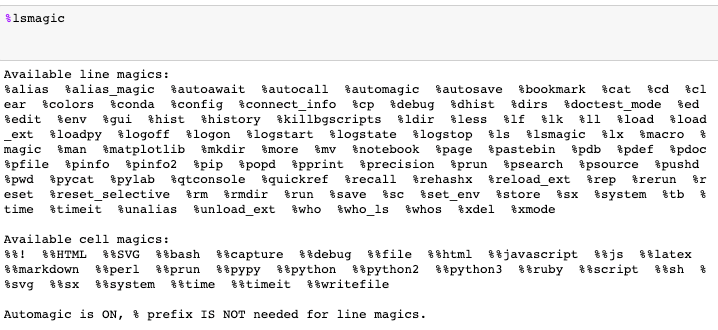
you might see all available magics with the help of%lsmagic.
Magic functions are callable without having to jot down the initial % if set to 1.

In fact, Github gist is also akin to pastebin albeit with version control.
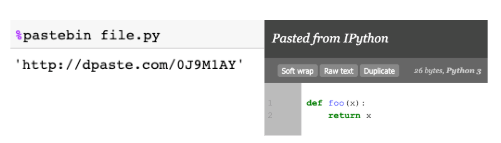
Consider a python scriptfile.pywith the following content:
Using %pastebin in Jupyter Notebook generates a pastebin url.
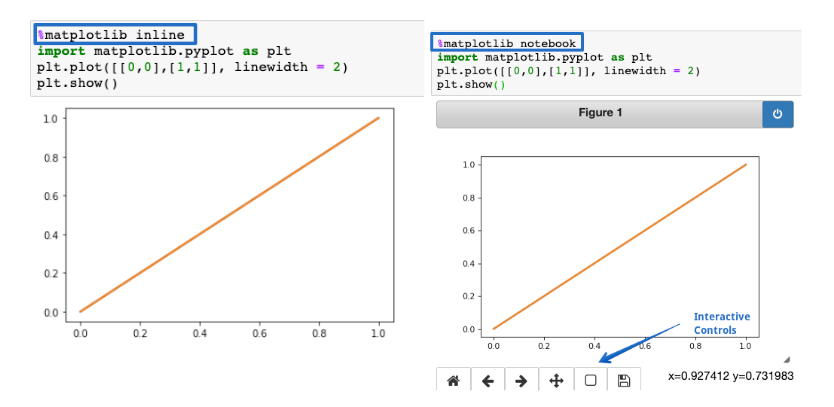
The%matplotlib inlinefunction is used to render the static matplotlib plots within the Jupyter notebook.

Try replacing theinlinepart withnotebookto get zoom-able & resize-able plots, easily.
verify the function is called before importing the matplotlib library.
The%runfunction runs a python script inside a notebook.

%%writefilewrites the contents of a cell to a file.
Here the code will be written to a file named foo.py and saved in the current directory.
The %%latex function renders the cell contents as LaTeX.
It is useful for writing mathematical formulae and equations in a cell.
This opens an interactive debugging environment that brings you to the position where the exception has occurred.
To exit the debugger hitq.
It is especially useful when printing dictionaries or JSON data.
Lets have a look at an example which uses bothprintandpprintto display the output.
The color of the note depends upon the key in of alert that is specified.

Just add any or all of the following codes in a cell that needs to be highlighted.
Now all the outputs get printed one after the other.
To revert to the original setting :
Running python scripts with the i option.
The originalsourceof the hack.
If yes then here is a shortcut that can undo that delete action.
In this article, Ive listed the main tips I have gathered while working with Python and Jupyter Notebooks.
Im sure these simple hacks will be of use to you at some point in your career.
Till then, happy coding!
This article was written byParul PandeyonTowards Data Science.

you’re able to read the original piecehere.
Also tagged with