But iOS 14.5 also introduced support for the newApple AirTag, which risks doing the opposite.
While clearly useful,AirTags can also potentially be misused.
Concerns have been raised they mightfacilitate stalking, for example.

And theres also a more fundamental issue with this technology.
Itseuphemistic descriptionas a crowdsourced way to recover lost items belies the reality of how these items are tracked.
It’s free, every week, in your inbox.

So, how exactly do AirTags work?
AirTags are small, circular metal discs, slightly larger and thicker than an Australian one-dollar coin.
Each tag transmits a unique identifier using Bluetooth.

The AirTags themselves have no positional location capability they do not contain GPS technology.
Rather, they merely ping the nearest Bluetooth-enabled equipment and let that devices location data do the rest.
Besides Bluetooth, AirTags also use a relatively new technology calledUltra Wideband.
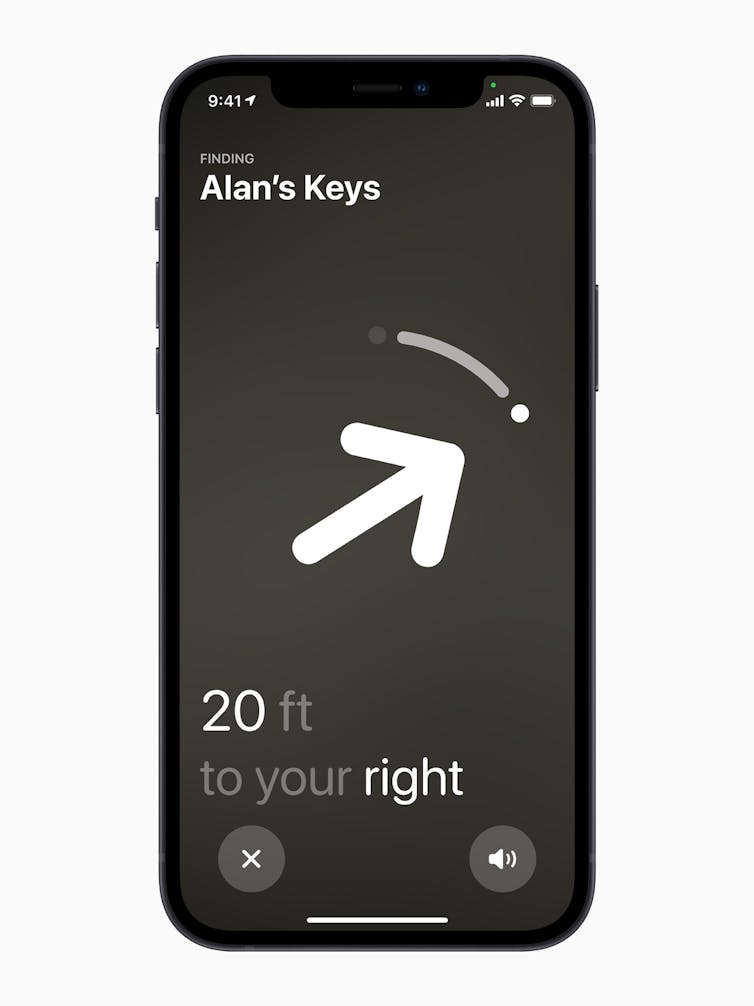
This precision extends to directional finding now, your phone can literally point you towards the missing tag.
Heres what Precision finding looks like on an iPhone paired with an AirTag.
Everyones iPhone (assuming Bluetooth is enabled) is listening for AirTags.

When it hears one, it uploads details of that tags identifier and the phones location to Apples servers.
Besides any privacy concerns, this also likely uses small amounts of your data allowance.
Stalking technology?
But these measures are relatively easy to circumvent.
This could be done by the victim returning home or within range of their stalker within athree-day window.
Just like other commonly encountered alerts, many users will tire of seeing them, and dismiss the prompts.