Deep reinforcement learning is one of the most interesting branches ofartificial intelligence.
But in this post, Ill attempt to demystify it without going into the technical details.
The environment provides information about the state of the system.
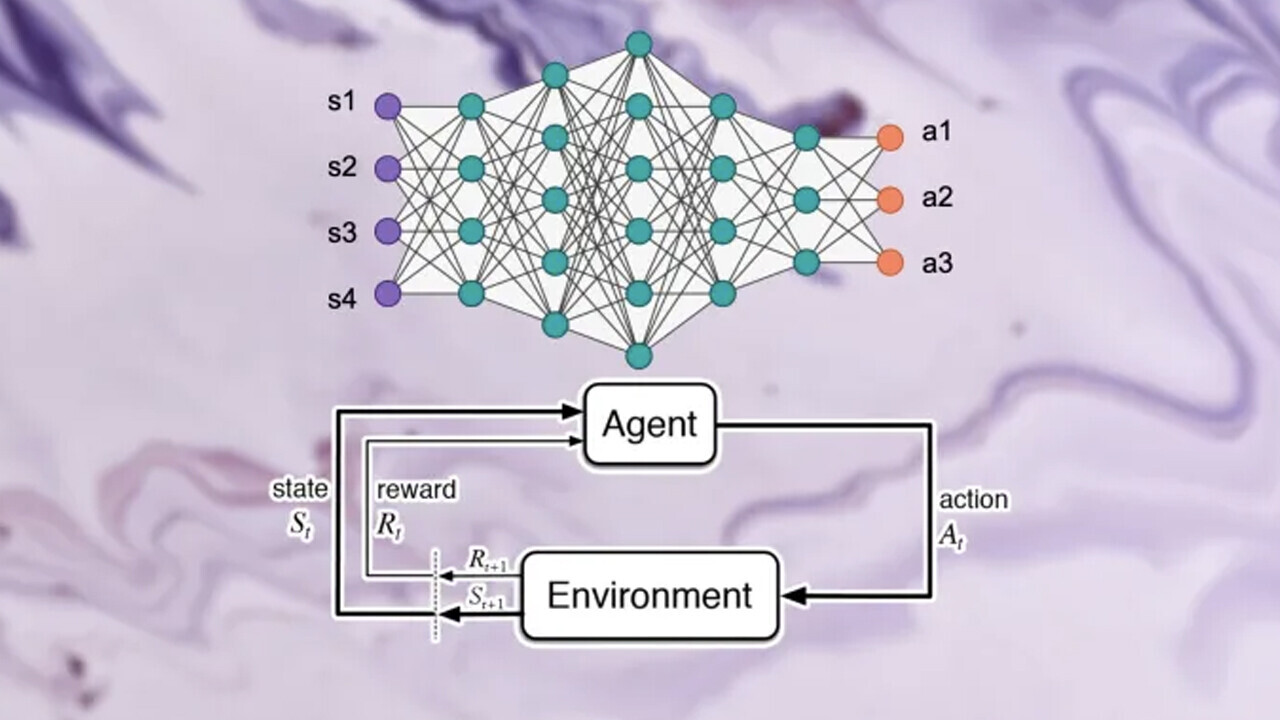
The agent observes these states and interacts with the environment by taking actions.
These actions cause the environment to transition to a new state.
40% off TNW Conference!

This series of steps is called an episode.
The goal of reinforcement learning is to train the agent to take actions that maximize its rewards.
The agents action-making function is called a policy.

An agent usually requires many episodes to learn a good policy.
For simpler problems, a few hundred episodes might be enough for the agent to learn a decent policy.
For more complex problems, the agent might needmillions of episodes of training.

There are more subtle nuances to reinforcement learning systems.
For example, an RL environment can be deterministic or non-deterministic.
In deterministic environments, running a sequence of state-action pairs multiple times always yields the same result.

Reinforcement learning applications
To better understand the components of reinforcement learning, lets consider a few examples.
Each game of chess is an episode.
The agent receives a reward for reaching the checkmate state and zero rewards otherwise.

Atari Breakout:Breakout is a game where the player controls a paddle.
Theres a ball moving across the screen.
Every time the paddle hits a brick, the brick gets destroyed and the ball bounces back.
In Breakout, the environment is the game screen.
The actions that the agent can take are move left, move right, or not move at all.
The RL agent observes the state of the environment through cameras, lidars, and other sensors.
But what exactly does the RL agent learn?
A policy maps states to actions.
First, it starts by making random moves, for which it receives no rewards.
In one of the episodes, it finally reaches the exit and receives the exit reward.
It gradually adjusts the policy until it converges to an optimal solution.
REINFORCE is a popular policy-based algorithm.
The advantage of policy-based functions is that they can be applied to all kinds of reinforcement learning problems.
Value-based algorithms:Value-based functions learn to evaluate the value of states and actions.
Value-based functions help the RL agent evaluate the possible future return on the current state and actions.
There are two variations to value-based functions: Q-values and V-values.
Q functions estimate the expected return on state-action pairs.
V functions only estimate the value of states.
Q functions are more common because it is easier to transform state-action pairs into an RL policy.
Two popular value-based algorithms are SARSA and DQN.
Value-based algorithms are more sample-efficient than policy-based RL.
Model-based algorithms:Model-based algorithms take a different approach to reinforcement learning.
Model-based reinforcement learning allows the agent to simulate different trajectories before taking any action.
Model-based approaches provide the agent with foresight and reduce the need for manually gathering data.
Non-deterministic environments, such as the real world, are very hard to model.
In some cases, developers manage to create simulationsthat approximate the real environment.
But even learning models of these simulated environments ends up being very difficult.
Nonetheless, model-based algorithms have become popular in deterministic problems such as chess and Go.
Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MTCS) is a popular model-based method that can be applied to deterministic environments.
For example, Actor-Critic algorithms combine the strengths of policy-based and value-based functions.
Why deep reinforcement learning?
Until now, weve said nothing about deep neural networks.
In fact, you’re able to implement all the above-mentioned algorithms in any way you want.
In these cases, youll need an approximation function that can learn optimal policies based on limited data.
And this is whatartificial neural networksdo.
This complex learning capacity can help RL agents to understand more complex environments and map their states to actions.
Deep reinforcement learning is comparable tosupervised machine learning.
The model generates actions, and based on the feedback from the environment, it adjusts its parameters.
However, deep reinforcement learning also has a few unique challenges that make it different from traditional supervised learning.
It might be able to learn an optimal policy based on the experiences it gathers across different training episodes.
But it might also miss many other optimal trajectories that could have led to better policies.
This added complexity increases the data requirements of deep reinforcement learning models.
Others think that reinforcement learning doesnt address some of the most fundamental problems of artificial intelligence.
you might read the original articlehere.