Key elements of this wave include machine intelligence, blockchain-based decentralized governance, and genome editing.
Naturally, they also reflect the bias inherent in the data itself.
It’s free, every week, in your inbox.

Depending on the design, it may learn that women are biased towards a positive result.
The key question to ask is notIs my model biased?, because the answer will always beyes.
The COMPAS system used a regression model to predict whether or not a perpetrator was likely to recidivate.

The COMPAS example shows how unwanted bias can creep into our models no matter how comfortable our methodology.
A small supervised model was trained on a dataset with a small number of features.
Yet, ordinary design choices produced a model that contained unwanted, racially discriminatory bias.
Had the team looked for bias, they would have found it.
This would have then worked to reduce unfair incarceration of African Americans, rather than exacerbating it.
The unwanted bias in the model stems from a public dataset that reflects broader societal prejudices.
Middle- and upper-class families have a higher ability to hide abuse by using private health providers.
Referrals to Allegheny County occur over three times as often for African-American and biracial families than white families.
With new developments in debiasing algorithms, Allegheny County has new opportunities to mitigate latent bias in the model.
Despite continuous lip service paid to diversity by tech executives,womenandpeople of colorremain under-represented.
Be aware of proxies: removing protected class labels from a model may not work!
We include an explanation of these metrics at the bottom of the article.
Some are preprocessing algorithms, which aim to balance the data itself.
Others are in-processing algorithms which penalize unwanted bias while building the model.
Yet others apply postprocessing steps to balance favorable outcomes after a prediction.
The particular best choice will depend on your problem.
Other libraries, such asAequitasand LIME, have good metrics for some more complicated modelsbut they only detect bias.
They arent capable of fixing it.
For instance, deep CNNs for image recognition are very powerful but not very interpretable.
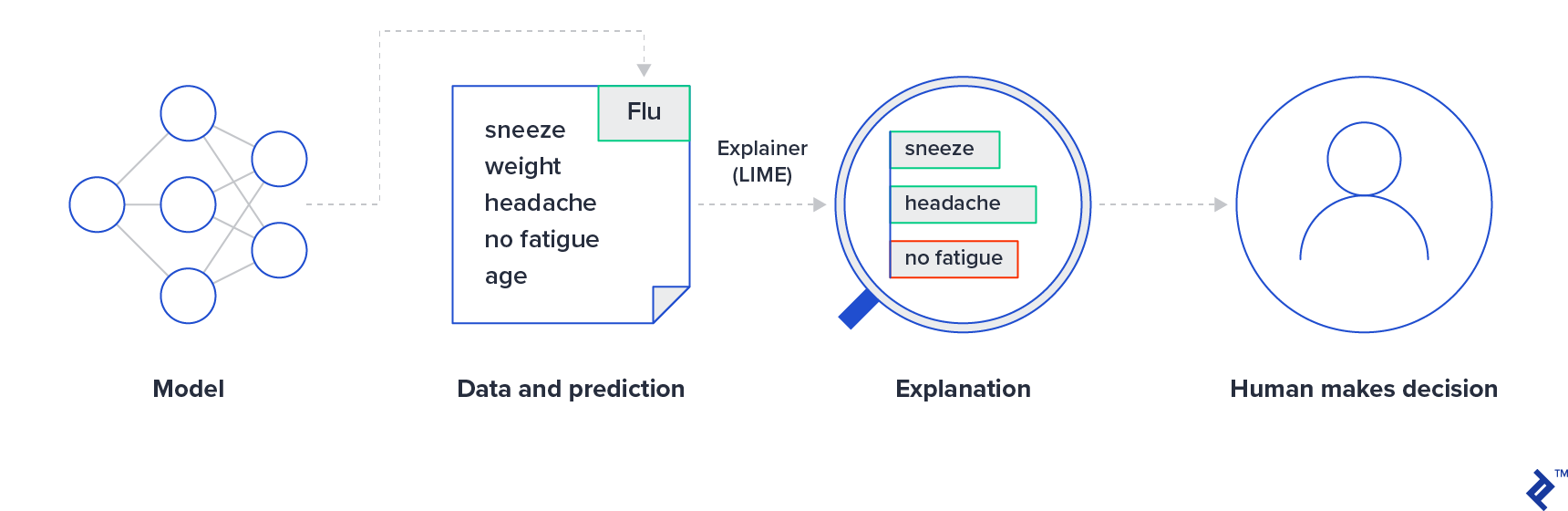
This process in a medical context is demonstrated with the image below.
Debiasing NLP models
Earlier, we discussed the biases latent in most corpora used for training NLP models.
If unwanted bias is likely to exist for a given problem, I recommendreadily available debiased word embeddings.
The GDPR isglobally the de facto standardin data protection legislation.
(But its not the only legislationtheres also Chinas Personal Information Security Specification, for example.)
The GDPR is separated into bindingarticlesand non-bindingrecitals.
We will zoom in on two key requirements and what they mean for model builders.
Prevention of discriminatory effects
The GDPR imposes requirements on the technical approaches to any modeling on personal data.
More general requirements can be found in Recital 71:
[.
useappropriate mathematical or statistical procedures, [.
ensure that therisk of errors is minimised[.
As outlined above, this may not be possible in all cases.
(However, the debate continues as to the extent of any bindingright to an explanation.)
Debate continues as to what an explanation would look like.
As the intelligence of machine learning models surpasses human intelligence, they also surpass human understanding.
Ensuring that AI is fair is a fundamental challenge of automation.
The famous example discussed in the paper of high equal opportunity difference is the COMPAS case.
As discussed above, African-Americans were being erroneously assessed as high-risk at a higher rate than Caucasian offenders.
This discrepancy constitutes an equal opportunity difference.