Machine learning has become an important component of many applications we use today.
And adding machine learning capabilities to applications is becoming increasingly easy.
Many ML libraries and online services dont even require a thorough knowledge of machine learning.
However, even easy-to-use machine learning systems come with their own challenges.
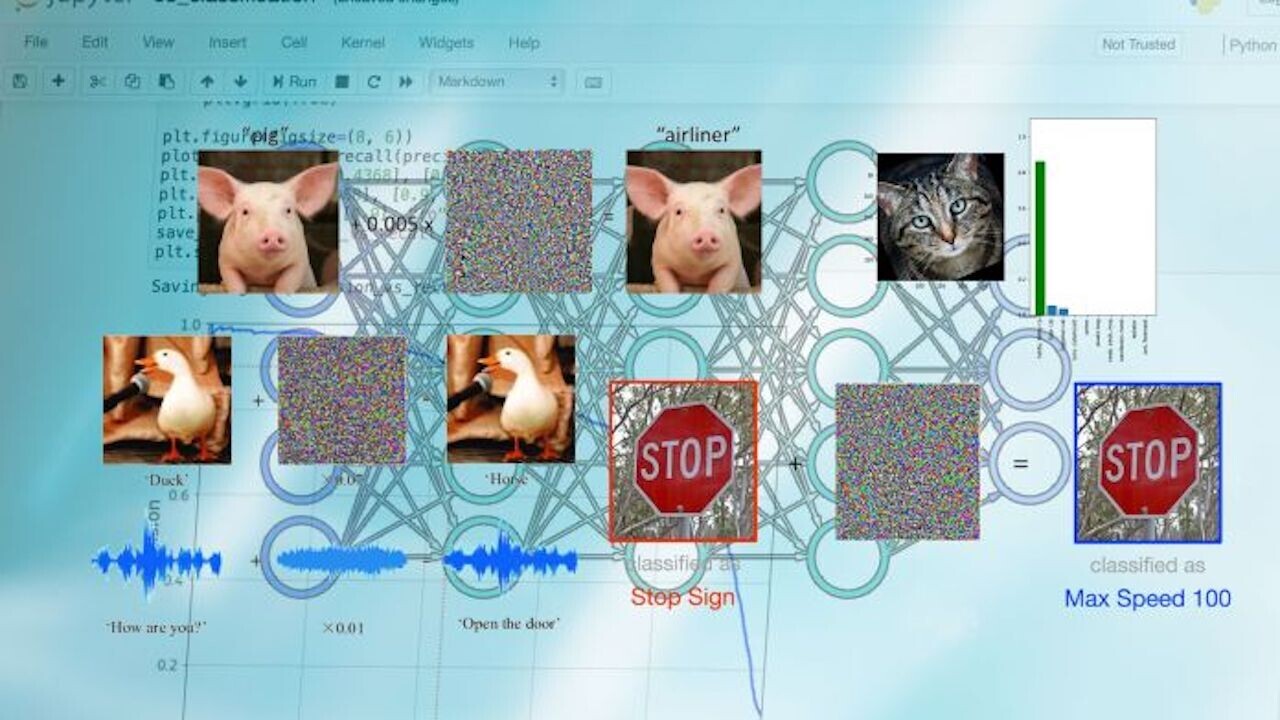
Among them is the threat ofadversarial attacks, which has become one of the important concerns of ML applications.
Adversarial attacks aredifferent from other types of security threatsthat programmers are used to dealing with.

It’s free, every week, in your inbox.
Software bugs are well-known among developers, and we have plenty of tools to find and fix them.
Static and dynamic analysis tools find security bugs.

Compilers can find and flag deprecated and potentially harmful code use.
Test units can check that functions respond to different kinds of input.
In a nutshell, although imperfect, the traditional cybersecurity landscape has matured to deal with different threats.

But the nature of attacks against machine learning and deep learning systems is different from other cyber threats.
You cant detect adversarial vulnerabilities with the classic tools used to harden software against cyber threats.
In recent years,adversarial exampleshave caught the attention of tech and business reporters.

One misconception about adversarial attacks is that it affects ML models that perform poorly on their main tasks.
Ideally, we want our models to be both accurate and robust against adversarial attacks.
2: Know the impact of adversarial attacks
In adversarial attacks, context matters.

In security systems, attackers can game the models to bypass facial recognition and other ML-based authentication systems.
Overall, adversarial attacks cause a trust problem with machine learning algorithms, especially deep neural networks.
Basically, we can divide the machine learning pipeline into the training phase and test phase.

In the test phase, the trained model is evaluated on examples it hasnt seen before.
If it performs on par with the desired criteria, then it is deployed for production.
Adversarial attacks that are unique to the training phase include data poisoning and backdoors.

Indata poisoning attacks, the attacker inserts manipulated data into the training dataset.
Test phase or inference time attacks are the types of attacks that target the model after training.
The most popular jot down is model evasion, which is the typical adversarial example that has become popular.
Another class of inference-time attacks tries to extract sensitive information from the target model.
For example,membership inference attacksuse different methods to trick the target ML model to reveal its training data.
Another important factor in machine learning security is model visibility.
Everyone else can see the models architecture and parameters, including attackers.
Having direct access to the model will make it easier for the attacker to create adversarial examples.
Black-box ML is harder to attack because the attacker only has access to the output of the model.
But harder doesnt mean impossible.
It is worth noting there are severalmodel-agnostic adversarial attacksthat apply to black-box ML models.
Adversarial robustness for machine learning really differentiates itself from traditional security problems, Chen says.
The security community is gradually developing tools to build more robust ML models.
But theres still a lot of work to be done.
Images, audio, and text files might seem innocuous per se.
But they can hide malicious patterns that can poison the deep learning model that will be trained by them.
What kind of data are you training your model on?
If youre using your own data to train your machine learning model, does it include sensitive information?
Who is the models developer?
Check the integrity of the models publisher.
Who else has access to the model?
You must set your defenses to account for such malicious behavior.
As Ive mentioned before, detecting adversarial tampering on data and model parameters is very difficult.
Therefore, you must see to it to detect changes to your data and model.
Researchers from academia and tech companies are coming together to develop tools to protect ML models against adversarial attacks.
TheAI Incident Databaseis a crowdsourced bank of events in which machine learning systems have gone wrong.
It can help you learn about the possible ways your system might fail or be exploited.
Machine learning needsnew perspectives on security.
Hopefully, these tips will help you better understand the security considerations of machine learning.
For more on the topic, see Pin-Yu Chens talk on adversarial robustness.
you’ve got the option to read the original articlehere.