Space debris is any nonfunctional human-made object in space.
Could this have been prevented?
What would have happened if there was damage?

And how will new commercial companies be regulated as space activities and launchesincrease exponentially?
For space law to be effective, itneeds to do three things.
First, regulation must prevent as many dangerous situations from occurring as possible.

Second, there needs to be a way to monitor and enforce compliance.
And finally, laws need to lay out a framework for responsibility and liability if things do go wrong.
So, how do current laws and treaties around space stack up?
What if a rocket landed on your house?
What would current law allow you to do?
40% off TNW Conference!

In 1978, the Soviet Cosmos 954 satellitefell into a barren region of Canadas Northwest Territories.
When it crashed, it spread radioactive debris from its onboard nuclear reactor over a wide swath of land.
When the Liability Convention was put into use in this context,four governing norms emerged.
But despite this and other incidences, Canada remains the only country to put the Liability Convention to use.
Currently, though, there isno globally coordinated space traffic management system.
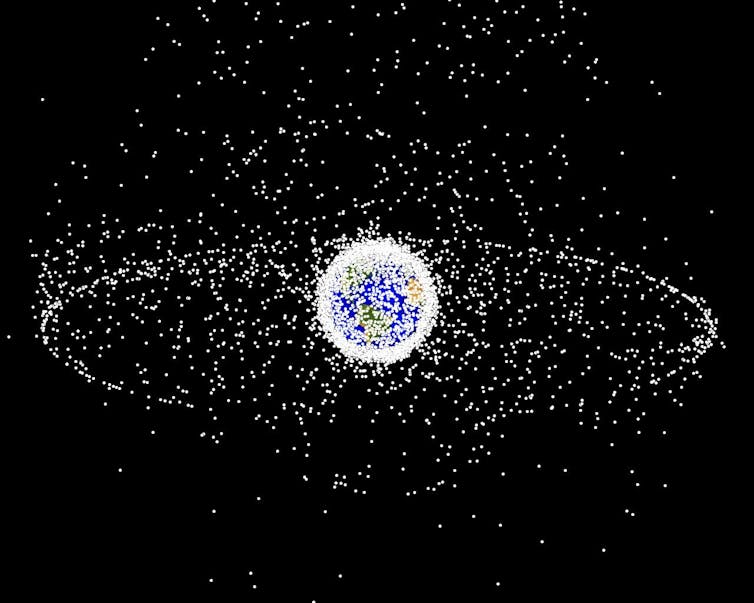
Every dot in this image represents a known piece of space debris.
But risks to life and property are not the only concerns about a busy sky.
The same is true for space, even if there is no clear direct victim or physical harm.
Space is shaping up to be a new frontier on which the tragedy of the commons can play out.
Such laws would not need to be invented from scratch.
The2007 United Nations Space Debris Mitigation guidelinesalready address the issue of debris prevention.
The chances of a person being killed by a falling satellite are close to zero.
This is an updated version of an article originally published on May 17, 2021.
It has been updated to clarify the history of falling space debris.