The human brain is said to be the mostcomplex biological structureever to have existed.
EnterNeuralink, a Silicon Valley start-up backed by Elon Musk that has developed aneuroprosthetic deviceknown as abrain-computer interface.
But is this possible?

Elon: Neuralink will definitely cure tinnitus.
The coin-sized Neuralink equipment, called a Link, isimplantedflush with the skull by a precision surgical robot.
The robot connects a thousand miniature threads from the Link to certain neurons.
Each thread is a quarter the diameter of a human hair.
40% off TNW Conference!
That includes people with paraplegia, quadriplegia, Parkinsons disease, and epilepsy.

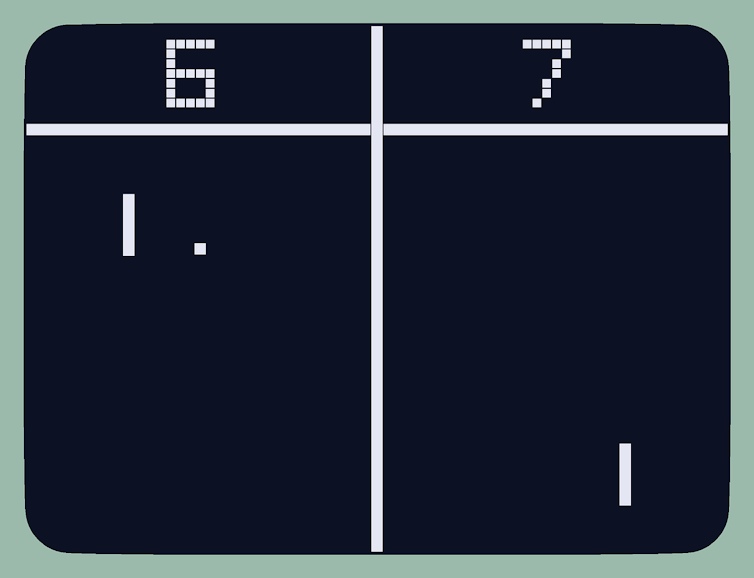
Pager the monkey played the computer game Pong with his mind.
Pager was shown how to play Pong using a joystick.
When he made a correct move, hed receive a sip of banana smoothie.
As he played, the Neuralink implant recorded the patterns of electrical activity in his brain.
This identified which neurons controlled which movements.
When the joystick was disconnected, Pager was able to play the game and win using only his mind.
Neuralink’s monkey can play Pong with its mind.
Musks tinnitus claims
Elon Muskhas claimedthe Neuralink unit could cure tinnitus by 2027.
A cure for tinnitus has provenelusive.
Treatment currently centers on masking the sound or learning to ignore it.
At present, the Neuralink prosthesis connects to the cerebral cortex, the surface layer of the brain.
This is where the rig can remedy damage to the brains ability to process motor sensory input or output.
Are Musks claims credible?
These claims might appear grandiose.
Yet the underlying science isnot controversial.
There has been much progress in the 60 years since then.
Neuroscientistsare broadlyoptimisticthe machine has the potential to treat tinnitus.
This throw in of technology has the potential to transform our treatments.
What do we need to be cautious of?
TheFDAcategorizes Neuralink as aclass III medical gear, the riskiest category.
Before human trials start, Neuralink must successfully dump the rigorous FDA regulatory controls.
Some monkeys have died during Neuralinks tests, andcritics have raised animal welfare concerns.
The approvals process for human testing could take some time.
The regulators will be looking for unintended negative consequences of the rig, such asdepression.
Once FDA-approved, Neuralink willenlisthuman volunteers and the next round of trials will proceed.
So its wise to not hold out false hope for an affordable implant in the short term.