Unlike the Earth, Jupiters atmosphere lacks a surface, so could be considered as a bottomless abyss.
40% off TNW Conference!
It can measure Jupiters magnetic field to determine the flows within deep, magnetized fluid layers.
And it can use microwave light to look straight through the clouds.
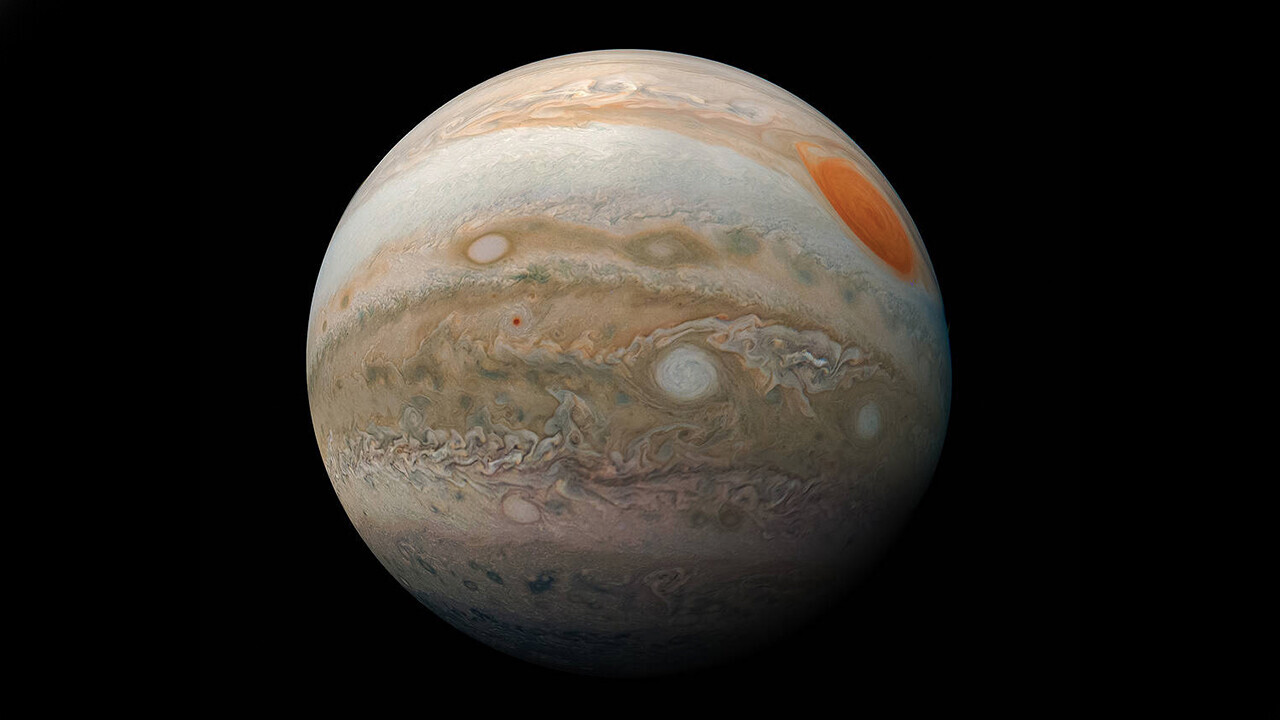
The Great Red Spot
JupitersGreat Red Spothas had a hard time in recent years.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
But fans of the storm can take comfort from Junos latest findings.
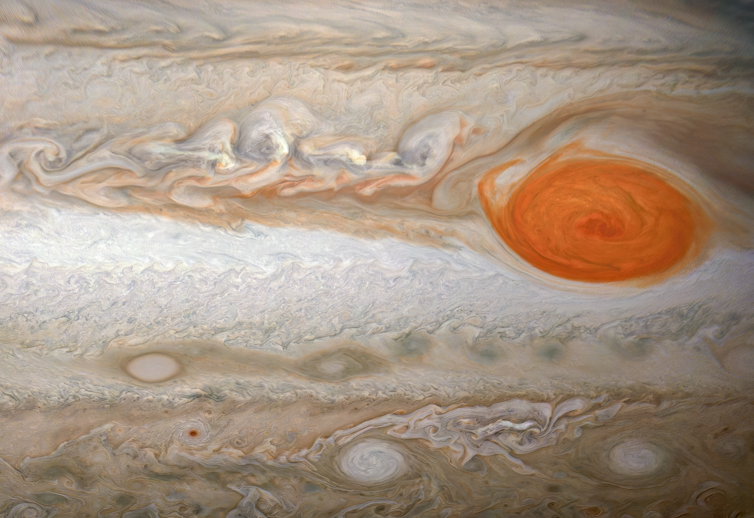

In 2017, Juno was able to observe the red spot inmicrowave light.
To place the depth in perspective, theInternational Space Station orbits ~420km above Earths surface.
The cool zones appeared dark, indicating the presence of ammonia gas, which absorbs microwave light.
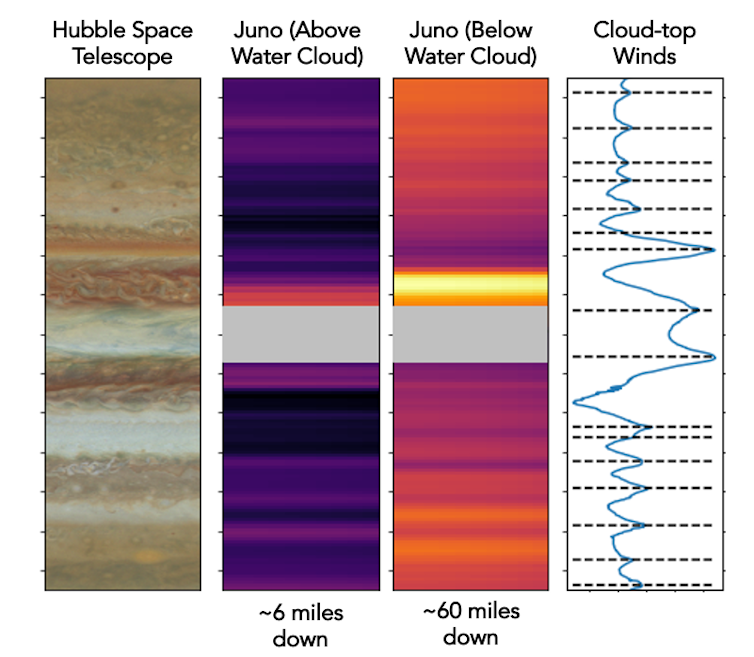
Conversely, the belts were bright in microwave light, consistent with a lack of ammonia.
But what happens when we probe deeper?
When Juno peered through this layer, it found something unexpected.

The belts became microwave-dark and the zones became microwave-bright.
A cline is a layer within a fluid where properties change dramatically.
Earths oceans have athermocline, dividing mixed surface waters from cold and deep water below.
He describes the balloon traveling down towards a Jovian thermocline and its associated bank of clouds.
The jovicline may separate the shallow cloud-forming weather layer from the deep abyss below.
This unexpected result implies something is moving all that ammonia around.
A conveyor belt?
The rising could cause ammonia enrichment and the sinking ammonia depletion.
If true, there would be abouteight of these circulation cellsin each hemisphere.
Other meteorological phenomena might be responsible for moving the ammonia around within this deep atmosphere.
As Juno embarks on itsextended mission, scientists will be working to make sense of these new findings.