(AI) and computer science that enables automated systems to see, i.e.
The projects are defined in terms of the:Goal, Methods,andResults.
The training and test data sets contain 60,000 and 10,000 labeled images, respectively.
The MNIST data set is well studied in literature with test accuracies in the range of 9699%.
For the Fashion MNIST data set, test accuracies are typically in the range 9096%.
Fig 2: Examples of OCT images from the Kaggle Dataset in [12].
Fig 3. qualitatively demonstrates the performance of the classification model.
Usage of Gradcam using thetf_explainlibrary is shown below.
Some well-known visualization and explainability libraries aretf_explainandLocal Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME).
The number of divided sub-regions can be manually provided as a parameter.
4 and code below.
Results:Using the proposed method, ROIs in most non-medical images should be explainable.
The major difference between this project and the prior projects is the format of data.
An example of the Google API for object detection on a new unseen image is shown in Fig.
5 and code below.
Extensions of the 2D bounding box detector to 3D bounding boxes specifically for autonomous drive are shown inthese projects.
6, 2) ROIs corresponding to pallor need to be displayed and tracked over time.
To fuse the outcomes from multiple pathology sites, early, mid and late fusion can be applied.
Results:The data for this work is available forbenchmarking.
Using the Deepdream algorithm the visualizations are shown in Fig.
Similarly, we observe differences in features between the inner and outer segments of the tongue.
These assessments are useful to create a personalized pathology tracking system for patients with anemia.
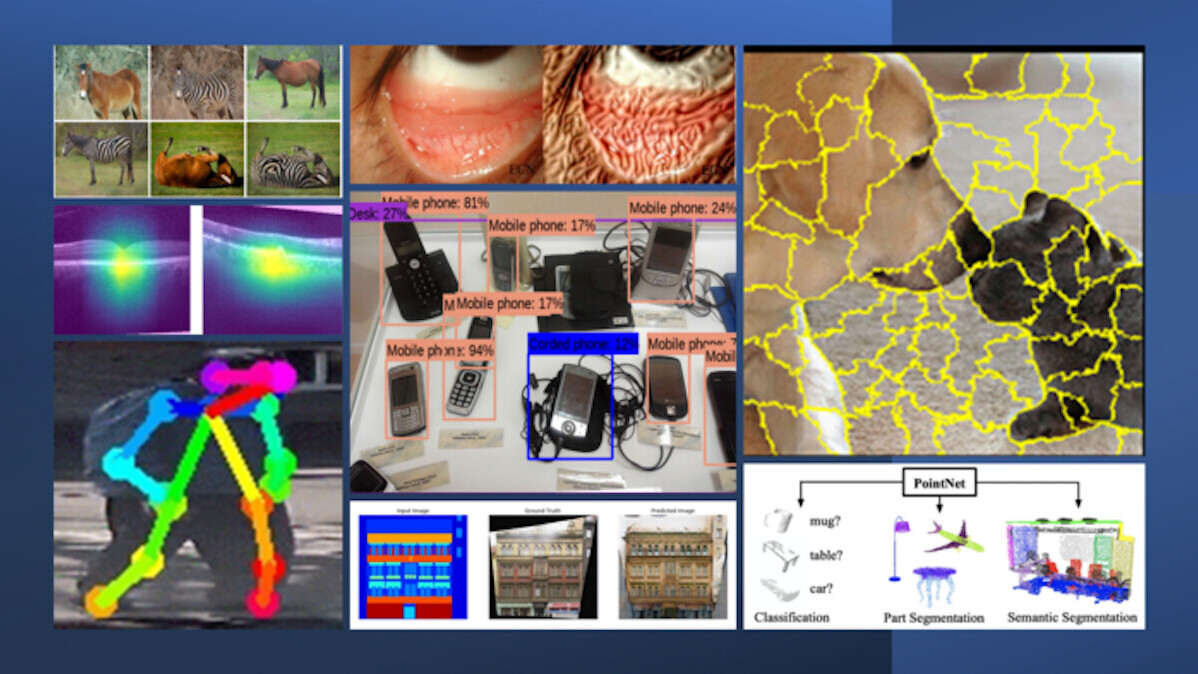
Project 6: Point cloud segmentation for object detection.
Next 1D convolutions are used to learn the shapenessfeatures using the Pytorch library in thePointnet colabas shown below.
Results:The outcome of the model can be summarized using Fig.
Extensions to this work can be useful for 3D bounding box detection for autonomous drive use cases.
This process is known asfeature encoding.
This combination of encoder-decoder pair enables the input and output to have similar dimensions, i.e.
input is an image and output is also an image.
Methods:The encoder-decoder combination with residual skip connections is popularly known as the U-net [15].
9 below (source here).
Thus, selecting the right training data set is significantly important for optimal outcomes.
[1819], as shown in Fig.
For this category of problems, keyframe information from multiple subsequent video frames is processed collectively to generatepose/intention-related predictions.
Higher the number of skeletal points, higher computational complexity is incurred.
Results:Qualitative results for the method above are shown in Fig.
11: Example of Pedestrian Intention prediction on the JAAD [18] data set.
12 and in theGAN Colab.
an image and its corresponding semantic segmentation is required for training purposes.
However, in instances where paired input and labels are unavailable, CycleGANs [17] can be useful.
In CycleGAN models, two sets of Generator/Discriminator combinations are used.
So at the end of a cycle, a doubly transformed version of image A is obtained.
Examples of CycleGAN output are shown in Fig.
These models can also be used for artistic transformations, image denoising and AR/VR transformations.
It is noteworthy that the output metrics can vary based on the image domain and use case.
Read the original articlehere.