Are we alone in the Universe?Billions of dollarsare being spent trying to answer that simple question.
The implications of finding evidence for life beyond Earth are staggering.
The before and after mark would punctuate human history.

Marsis currently the most popular exploration target to search for evidence of life elsewhere.
Windows into the past
Today Mars is cold and inhospitable.
But it may have been more Earth-like and habitable in a bygone era.

Landforms on Mars record the action of liquid surface water, perhaps as early as 3.9 billion years ago.
Giant impacts both destroy and create favorable environments for life.
40% off TNW Conference!
Samples collected by rovers will be returned in future missions.
For now, meteorites are the only samples of Mars available to study here on Earth.
Martian meteorites are born when an impact on Mars ejects rocky fragments that later intercept Earths orbit.

Most Martian meteorites are igneous rocks, such as basalt.
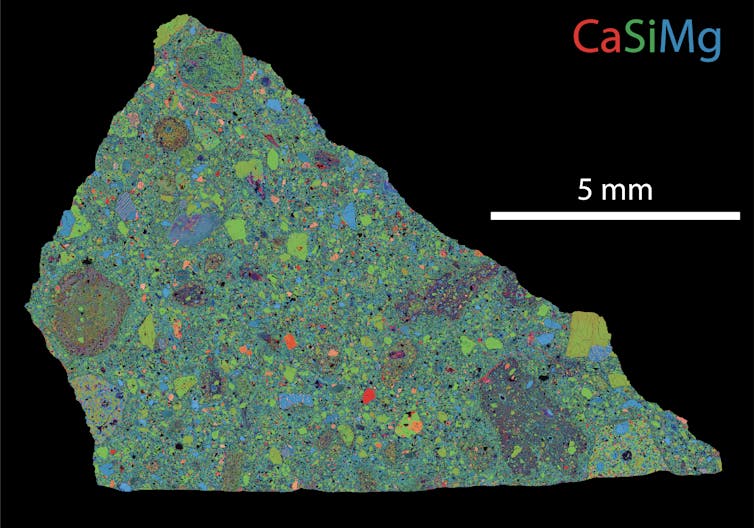
Meteorite NWA 7034 has been dubbed Black Beauty.
Unique oxygen isotope signatures reveal its origin from Mars.

Other meteorites blasted off of Mars during the same event have since been found.
NWA 7034 is a complicated rock made of broken rock and mineral shards called breccia.
Its various fragments record different snippets of Martian history.
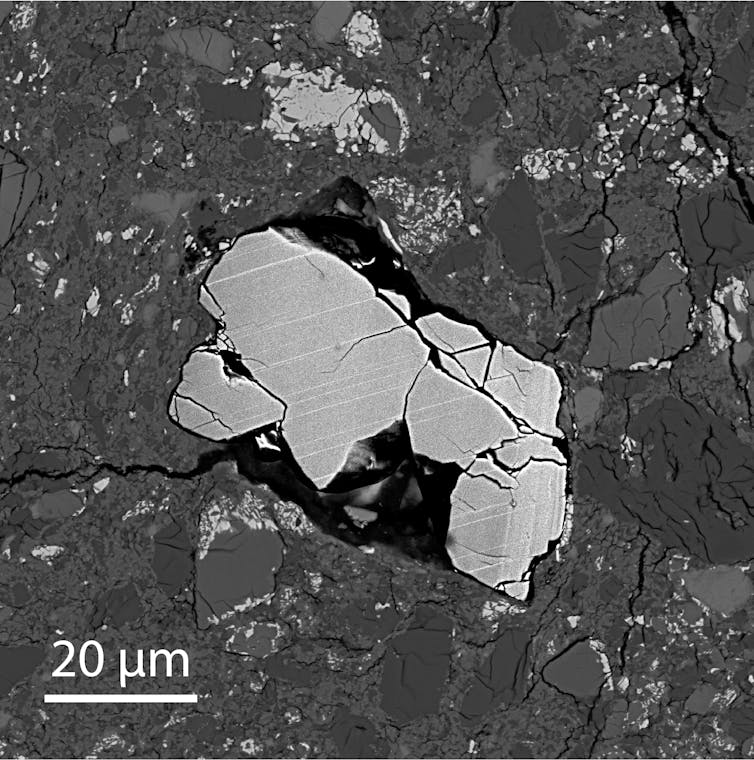
Tiny grains of the mineral zircon occur in NWA 7034.
Zircon is quite useful for studying meteorite impacts.
However, no zircons with definitive shock damage had been identified in previous studies of NWA 7034.
NWA 7034 is similar to a bang out of sedimentary rock on Earth called conglomerate.
In such rocks, every mineral can have a different origin.
We looked at more than 60 zircons, but found only one shocked grain.
This means the impact occurred before the grain was mixed into the pile of fragments that became a rock.
Reassessing Marss timelines
The throw in of shock features we found are called deformation twins.
High-pressure shock waves squeeze zircon like an accordion.
We dont know what kind of rock the shocked zircon originally formed in.
The original igneous host rock was ripped apart during impacts on Mars.
The zircon is a broken fragment from a larger grain mixed in with the matrix of the meteorite.
We do, however, know where shocked zircons like this are made.
On Earth, shocked zircons with deformation twins are only found at impact craters.
Moreover, they occur at all of Earths largest asteroid strikes.
In this case, shocked zircons were one product of an impact large enough to cause a mass extinction.
It was further proposed that habitable conditions existed as of 4.2 billion years ago.
However, the shocked zircon we found crystallized 4.45 billion years ago.
When exactly was the impact?
Bothlandformsandwater-bearing mineralsargue for early surface water on Mars, possibly by 3.9 to 3.7 billion years ago.
This may be the best indicator for when habitable conditions existed.
Our findings raise new questions about the early impact history of Mars.