The cause of this more thanUS$50 millionfailure was a geomagnetic storm because of the Sun.
Geomagnetic storms occur when space weather hits and interacts with the Earth.
And engineers like me are working to better understand these risks and defend satellites against them.
What causes space weather?
The Sun is always releasing a steady amount of charged particles into space.
This is called the solar wind.

The Sun occasionally blasts huge amounts of particles into space during active events like solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
Solar wind also carries with it the solar magnetic field.
Sometimes, localized fluctuations on the Sun willhurl unusually strong bursts of particles in a particular direction.
It’s free, every week, in your inbox.
Normally,solar wind travels at roughly 900,000 mph(1.4 million kph).
But strong solar events can release winds up to five times as fast.
The strongest geomagnetic storm on record was because of acoronal mass ejection in September 1859.

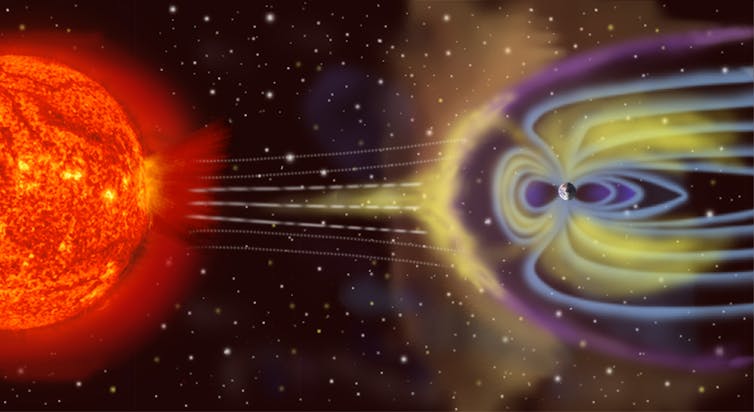
Thankfully, Earths magnetic field does a lot to protect humanity.
The first thing solar wind hits as it approaches Earth is the magnetosphere.
This region surrounding the Earths atmosphere is filled with plasma made of electrons and ions.

Its dominated by the planets strong magnetic field.
When solar wind hits the magnetosphere, it transfers mass, energy and momentum into this layer.
The magnetosphere can absorb most of the energy from the everyday level of solar wind.
When the atmosphere absorbs energy from magnetic storms, it heats up and expands upward.
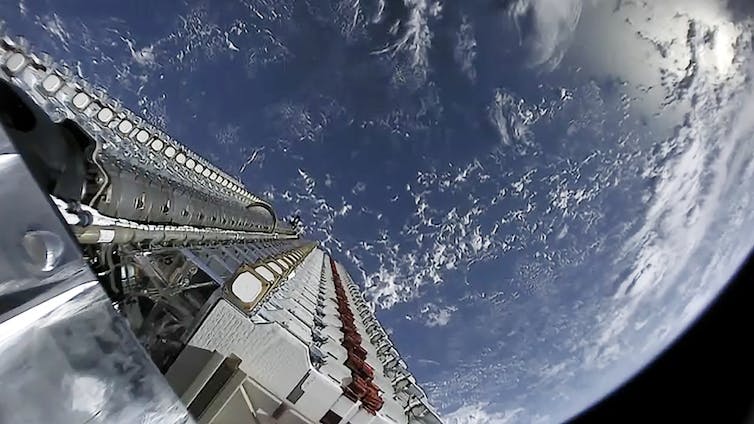
Higher density meansmore drag, which can be a problem for satellites.
The latest batch of Starlink satellites encountered a geomagnetic storm while still in very low-Earth orbit.
Drag is just one hazard that space weather poses to space-based assets.
This buildup of electrons candischarge in what is basically a small lightning strikeand damage electronics.
Small errors are common and usually fixable, buttotal failures, though rare, do happen.
Finally, geomagnetic storms can disrupt the ability of satellites to communicate with Earth using radio waves.
Many communications technologies, like GPS, for example,rely on radio waves.
The atmosphere alwaysdistorts radio waves by some amount, so engineers correct for this distortion when building communication systems.
The calibrations in place for a quiet atmosphere become wrong during geomagnetic storms.
Autonomous driving systems will require accurate positioning as well.
Some of the risks can be minimized byshielding electronics from radiationordeveloping materialsthat are more resistant to radiation.
But there is only so much shielding that can be done in the face of apowerful geomagnetic storm.
The mission went ahead anyway.
The Sun is like a child that often throws tantrums.
Its essential for life to go on, but its ever-changing disposition make things challenging.