Do you keep hearing people talk about sampling rate in music?
Butarent certain what that actually is??
Well, friend, youve come to the right place.
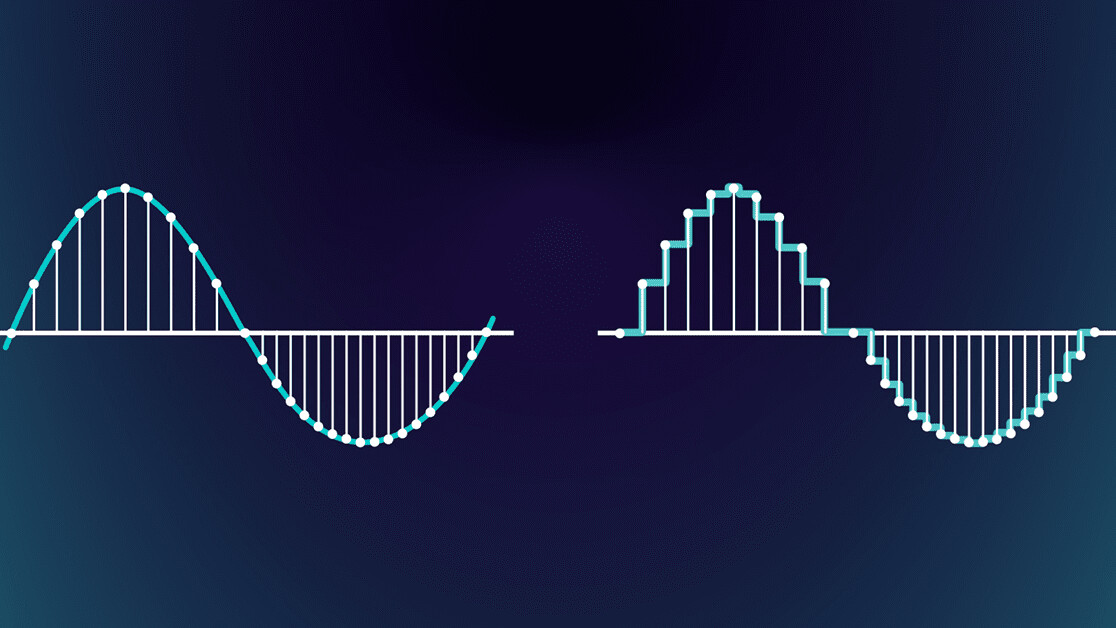
On a fundamental level, sampling rate is a result of the digitization of audio.
But were getting ahead of ourselves.
Sampling rate in audio is literally the number of samples taken per second.

This is measured in Hertz (Hz).
[Read:How do you build a pet-friendly gadget?
It’s free, every week, in your inbox.

Now, the common rate is that of CDs or FLAC, which is a lossless audio file.
This clocks in at 44.1kHz.
Weve already touched on the accuracy issue (i.e.

the higher the sampling rate, the higher the quality), but its not quite that simple.
Sampling rate is directly related to frequency, in other words the highest sound that can be accurately reproduced.
Lets look at the common 44.1kHz figure we discussed earlier.

This allows sounds of up to 22kHz to be played back.
The reason its this frequency and not 44.1kHz is all down tothe NyquistShannon Theorem.
If you want to know more,it’s possible for you to go and read about it here.
Heres a picture, because why not?
Do you remember earlier when I said sampling rate impacts quality, but only up to a point?
Nows the time to resolve that.
The limits of human hearing stretch from20Hz to 20kHz.
The truth is though that the majority of people cannot hear anywhere near these high.
The average upper limit for adults is betweenbetween 15kHz and 17kHz.
What this means is that CDs and many FLAC files play music with frequenciesbeyond what humans can hear.
Of course, this is a contentious topic.
I will say this though: Im talking about this from the perspective of a music consumer.
TL;DR
Sampling rate can be seen as the audio version of frames per second.
It is the number of clips taken from an analogue sound wave so that make it a digital file.
There we go, people!
Some analysis on what sampling rate is,just for you.