It is mainly used for advanced applications in natural language processing.
Google is using it to enhance its search engine results.
OpenAI has used transformers to create its famous GPT-2 andGPT-3models.
They have been used for time series forecasting.
Researchers are still exploring ways to improve transformers and use them in new applications.
Here is a brief explainer about what makes transformers exciting and how they work.

It’s free, every week, in your inbox.
The classicfeed-forward neural networkis not designed to keep track of sequential data and maps each input into an output.
This works for tasks such as classifying images but fails on sequential data such as text.

The meaning of words can change depending on other words that come before and after them in the sentence.
Before transformers,recurrent neural networks(RNN) were the go-to solution for natural language processing.
This enables it to keep track of the entire sentence instead of processing each word separately.

Recurrent neural nets had disadvantages that limited their usefulness.
First, they were very slow.
Second, they could not handle long sequences of text.

And third, they only captured the relations between a word and the words that came before it.
In reality, the meaning of words depends on the words that come both before and after them.
But LSTMs were even slower to train than RNNs and still couldnt take full advantage of parallel computing.

They still relied on the serial processing of text sequences.
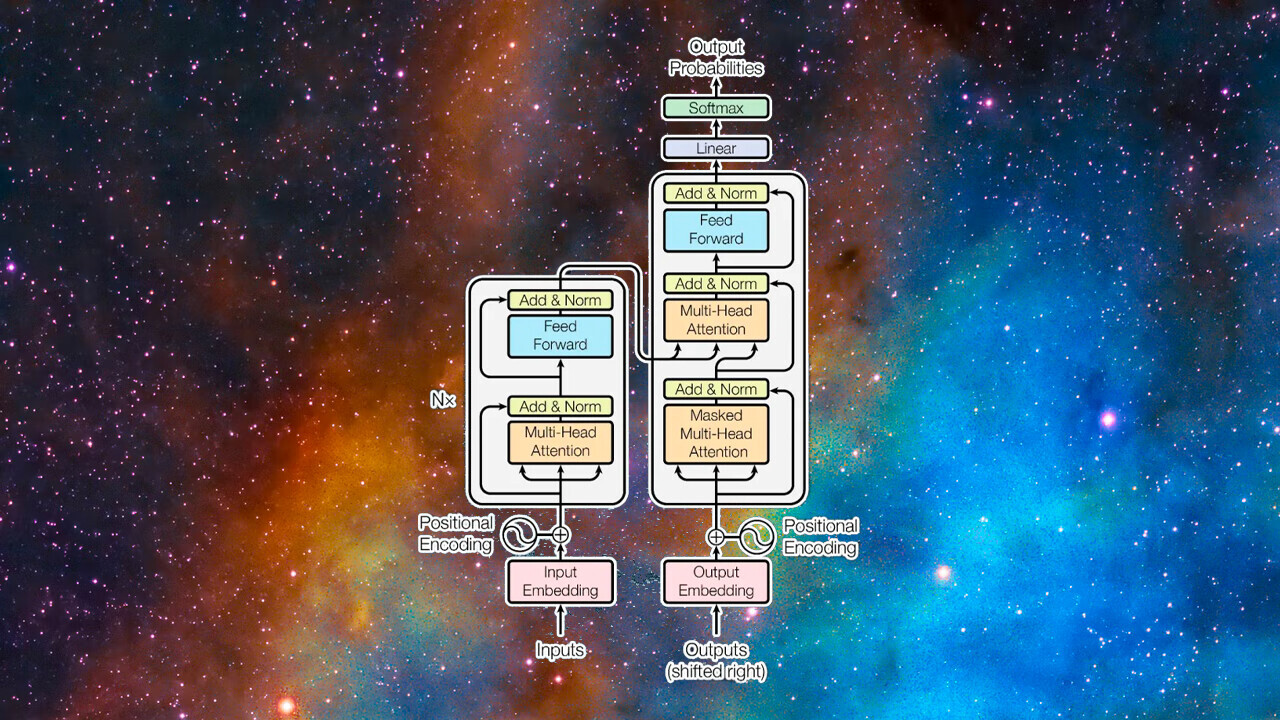
Transformers, introduced in the 2017 paper Attention Is All You Need, made two key contributions.
Despite their differences, all these types of models have one thing in common.

The job of a neural online grid is to transform one key in of data into another.
The decoder module transforms the encoded vector into a string of text in the destination language.
The tokenization algorithm can depend on the program.

In most cases, every word and punctuation mark roughly counts as one token.
Some suffixes and prefixes count as separate tokens (e.g., ize, ly, and pre).
The tokenizer produces a list of numbers that represent the token IDs of the input text.
The tokens are then converted into word embeddings.
A word embedding is a vector that tries to capture the value of words in a multi-dimensional space.
However, cat is closer to lion than wolf across some other dimension that separates felines from canids.
Similarly, Paris and London might be close to each other because they are both cities.
However, London is closer to England and Paris to France on a dimension that separates countries.
Word embeddings usually have hundreds of dimensions.
Word embeddings are created by embedding models, which are trained separately from the transformer.
There are several pre-trained embedding models that are used for language tasks.
Unlike RNN and LSTM models, the transformer does not receive one input at a time.
It can receive an entire sentences worth of embedding values and process them in parallel.
Next, the input is passed to the first encoder block, which processes it through an attention layer.
The attention layer tries to capture the relations between the words in the sentence.
Here, the model must associate it with cat and its with bottle.
Accordingly, it should establish other associations such as big and cat or crossed and cat.
The attention layer contains multiple attention heads, each of which can capture different kinds of relations between words.
Transformers contain several blocks of attention and feed-forward layers to gradually capture more complicated relationships.
Like the encoder module, the decoder attention vector is passed through a feed-forward layer.
The encoder module receives and processes the full input string.
But not all transformer applications require both the encoder and decoder module.
For example, the GPT family of large language models uses stacks of decoder modules to generate text.
BERT, another variation of the transformer model developed by researchers at Google, only uses encoder modules.
The advantage of some of these architectures is that they can be trained throughself-supervised learningorunsupervised methods.
By continuously going through this process, BERT captures the statistical relations between different words in different contexts.
Using unsupervised and self-supervised pretraining reduces the manual effort required to annotate training data.
Researchers are still finding ways to squeeze more out of transformers.
Transformers have also created discussions aboutlanguage understanding and artificial general intelligence.
But they are exciting and useful nonetheless and have a lot to offer.
you’re able to read the original articlehere.