The human brain is designed to make quick and effective decisions rather than stick to facts at all times.
Instead of acting rationally, we prefer to act fast.
With this article, youre going to learn
Ready to find out how our brains work?

The two widely acclaimed scientists were researching peoples innumeracy.
40% off TNW Conference!
In other words, its all about theframingof information.

We focus on different aspects depending on the surroundings.
Because of that, our reasoning is not fully rational.
A $110 saving changes the perspective, doesnt it?
This popular case is just the tip of the iceberg.
The same rules that affect how the users make decisions apply to UX designers.
As weve already mentioned above, were all prone toframing.
The context, as well as our previous experiences, all affect design decisions.
All these external factors make us focus on specific aspects of the issue or ignore the other ones.
Kathryn Whitenton of theNielsen Norman Groupused a brilliant example to describe how this works for UX designers.
Imagine that youve conducted a usability test with 20 users.
The outcomes can be described in two different ways
See the difference?
The researchers from Nielsen Norman Group decided to test both versions in an online quiz.
Heres what happened: 39% of UX designers who saw the success rated voted for a redesign.
This shows how framing research results and statistics in a different manner may lead to significantly different design decisions.
On the other hand, theframing biascan affect the users too.
Ready to learn more?
Because people use it to make decisions, its also a judgment heuristic, exactly like framing.
How it works for the user: Anchoring bias can be hugely helpful in understanding user interfaces.
This goes in line with theprinciple of least effortandJakobs law.
Were describing these two in our in-depth article aboutpsychological principles in UX.
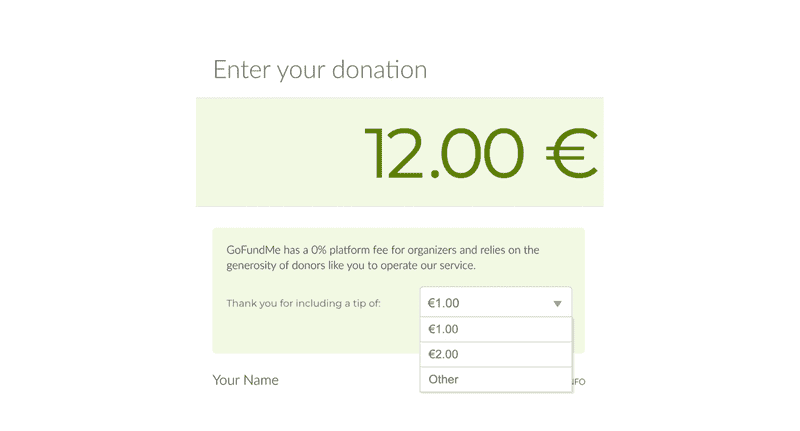
Suggested valuesare also a good example here.
Most non-profit websites, such asGoFundMe, dont charge a set fee for their services.
Its good to keep that in mind foruser testing.
It takes place if the question itself influences the answer.
How it works for the UX researcher: The wording bias largely affects the validity of surveys.
It happens because we dont want our efforts to go to waste.
Whats more,some studies suggestthat losses are perceived as psychologically twice more important than gains!
For instance, losing $100 hurts more than gaining 100$ satisfies.
The same rules apply to user experience design.
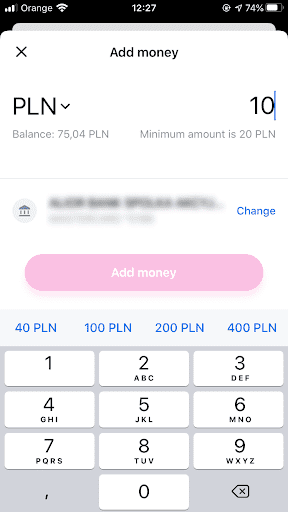
This often means that youre obliged to have more money in your account than you first needed.
Because of that, youre likely to use Revolut more often.
Whats more, suggested top-up amounts right above the keyboard fulfill the same function.
One of the ways to avoid this is throughagile development.
Short sprints and iterations make it easier to apply changes along the way and avoid wasting resources.
How it works for the user: Whats interesting, the social desirability bias typically appears unconsciously.
Most of the time, the respondents dont realize that they respond in a kinder, more favorable manner.
This bias can be avoided throughindirect questions.
This way, they wont feel the urge to appear as nice and friendly.
Key takeaways and cognitive biases reading list
The most important finding?
Were all prone to cognitive biases and the best we can do is tostay aware.
Educating yourself about psychological principles that affect our minds is sure to pay off in the long run.
She is based in Krakow, Poland.
you could read the original articlehere.